8 Min Read
8 Min Read
How Can NRI Invest in Indian Stock Market: Complete Guide to PIS Account, Demat Setup and Trading Requirements
How Can NRI Invest in Indian Stock Market: Complete Guide to PIS Account, Demat Setup and Trading Requirements
How Can NRI Invest in Indian Stock Market: Complete Guide to PIS Account, Demat Setup and Trading Requirements
Learn how NRIs can invest in Indian stocks through PIS accounts. Complete guide covering demat setup, documentation, trading rules and account requirements.
Learn how NRIs can invest in Indian stocks through PIS accounts. Complete guide covering demat setup, documentation, trading rules and account requirements.
Learn how NRIs can invest in Indian stocks through PIS accounts. Complete guide covering demat setup, documentation, trading rules and account requirements.

How Can NRI Invest in Indian Stock Market: PIS Guide
How Can NRI Invest in Indian Stock Market: PIS Guide
|
February 4, 2026
February 4, 2026



Stock market regulations under FEMA 2000 permit Non-Resident Indians to purchase equity shares through Portfolio Investment Scheme accounts. RBI data shows NRI investment in Indian securities reached ₹14,01,673 crores as of December 2024 (Reserve Bank of India). NSE and BSE provide market access through designated bank channels with specific compliance requirements.
Do bank representatives give contradictory information about NRE versus NRO accounts for stock trading with repatriation rights?
Are PIS permission delays from RBI pushing back your investment timeline by 30-45 days despite having funds ready?
Does the mandatory delivery-based trading requirement limit your ability to capture intraday price movements in volatile markets?
Secondary market participation requires four linked accounts working together. Banks open PIS-designated accounts separate from regular NRI accounts. Brokers provide demat and trading accounts with restricted features. Each account serves a specific regulatory function affecting fund flow.
Key Takeaways
Portfolio Investment Scheme accounts through RBI-designated banks form the mandatory channel for buying and selling equity shares on NSE and BSE
NRE accounts provide full repatriation rights after capital gains tax while NRO accounts face annual transfer caps for moving proceeds abroad
Intraday trading prohibitions restrict NRIs to delivery-based purchases only with shares settling in demat accounts on T+1 timeline
Documentation requirements include passport with valid visa proof, PAN card, overseas address verification, and foreign bank statements
Individual holding caps limit any single NRI to five percent of company paid-up capital with total NRI investment restricted to ten percent
Tax deduction at source applies automatically on capital gains before crediting sale proceeds with different rates for holding periods
Account linking sequence matters: open bank account first, secure PIS permission second, then establish demat and trading access third
Can NRI Invest in Indian Stock Market
Yes, NRIs can purchase and sell equity shares under FEMA regulations administered by RBI. The Foreign Exchange Management Act provides the legal framework. SEBI governs trading conduct and market operations.
Non-Resident Indians access secondary markets through designated channels only. You cannot open regular resident trading accounts. The system requires specific account types with additional verification layers.
Regulatory Framework
RBI controls foreign exchange aspects through FEMA guidelines. Portfolio Investment Scheme falls under Schedule 3 of FEMA regulations. SEBI sets trading rules for all market participants. NRIs follow different guidelines compared to residents. Compliance checks happen at multiple levels.
Investment Routes Available
Two main routes exist for NRI equity investments. PIS route handles secondary market trading on stock exchanges. Non-PIS route serves IPO subscriptions and mutual fund investments. Your choice between NRE and NRO accounts determines repatriation rights later.
Key Investment Guidelines and Trading Options for NRIs
Trading permissions come with specific boundaries. RBI and SEBI impose these limits to prevent market manipulation.
1. Permitted Investment Instruments
Equity Shares: NRIs can buy shares of companies listed on NSE and BSE. Both repatriation and non-repatriation basis investments work.
Convertible Debentures: Debentures converting into equity shares are permitted. Holdings count toward overall investment limits.
Mutual Funds: MF investments don't need PIS accounts. Direct purchase through NRE or NRO accounts works.
IPO Subscriptions: Primary market investments bypass PIS requirements. Allotted shares later need PIS accounts if selling.
2. Sector Investment Restrictions
Atomic energy projects cannot receive foreign capital. Railways infrastructure falls under similar restrictions. Lottery and gambling businesses stay prohibited. Defense manufacturing requires government approval. Banking sector investments follow separate FDI guidelines.
3. Trading Restrictions
Delivery-Based Only: All purchases must settle into your demat account. T+1 settlement means shares transfer one day after trade date. Same-day buy and sell transactions get automatically blocked.
Shareholding Caps: No single NRI can own more than five percent of any company's paid-up capital. Total NRI ownership caps at ten percent of company capital. Companies can increase this to twenty-four percent through shareholder resolution.
Derivatives Trading: Futures and options need SEBI-registered custodian appointment. Only NRO accounts work for F&O trading. Equity and index derivatives are permitted instruments.
Account Requirements: NRE Account, NRO Account, and PIS Permission
Three account types form the foundation of NRI stock investments. Setting them up correctly prevents transaction failures.
NRE Account (Non-Resident External)
NRE accounts hold foreign earnings converted to rupees. Salaries from overseas jobs go here. Full repatriation rights remain tax-free in India. Interest earned avoids Indian income tax completely. Only capital gains tax applies when selling stocks.
NRO Account (Non-Resident Ordinary)
NRO accounts manage India-sourced income exclusively. Rent from Indian property goes here. Annual transfers abroad cap at one million US dollars. Interest faces tax deduction at source. Mixing foreign and Indian income violates regulations.
PIS-Designated Account Setup
Stock transactions require separate PIS-linked accounts. NRE holders need NRE PINS accounts. NRO holders need NRO settlement accounts. Only one PIS account permitted per NRI nationwide.
Banks apply to RBI for your PIS authorization. Approval results in a unique permission letter containing permission number and trading limits. Brokers need this letter before opening demat accounts.
Demat and Trading Account Linking
Your demat account must link to PIS bank account correctly. NRE demat connects with NRE PINS accounts. NRO demat links to NRO settlement accounts. Brokers provide trading platforms after account linking completes.
NRE vs NRO: Choosing Between Investment Routes
Your account choice affects taxes, fund movement, and compliance requirements.
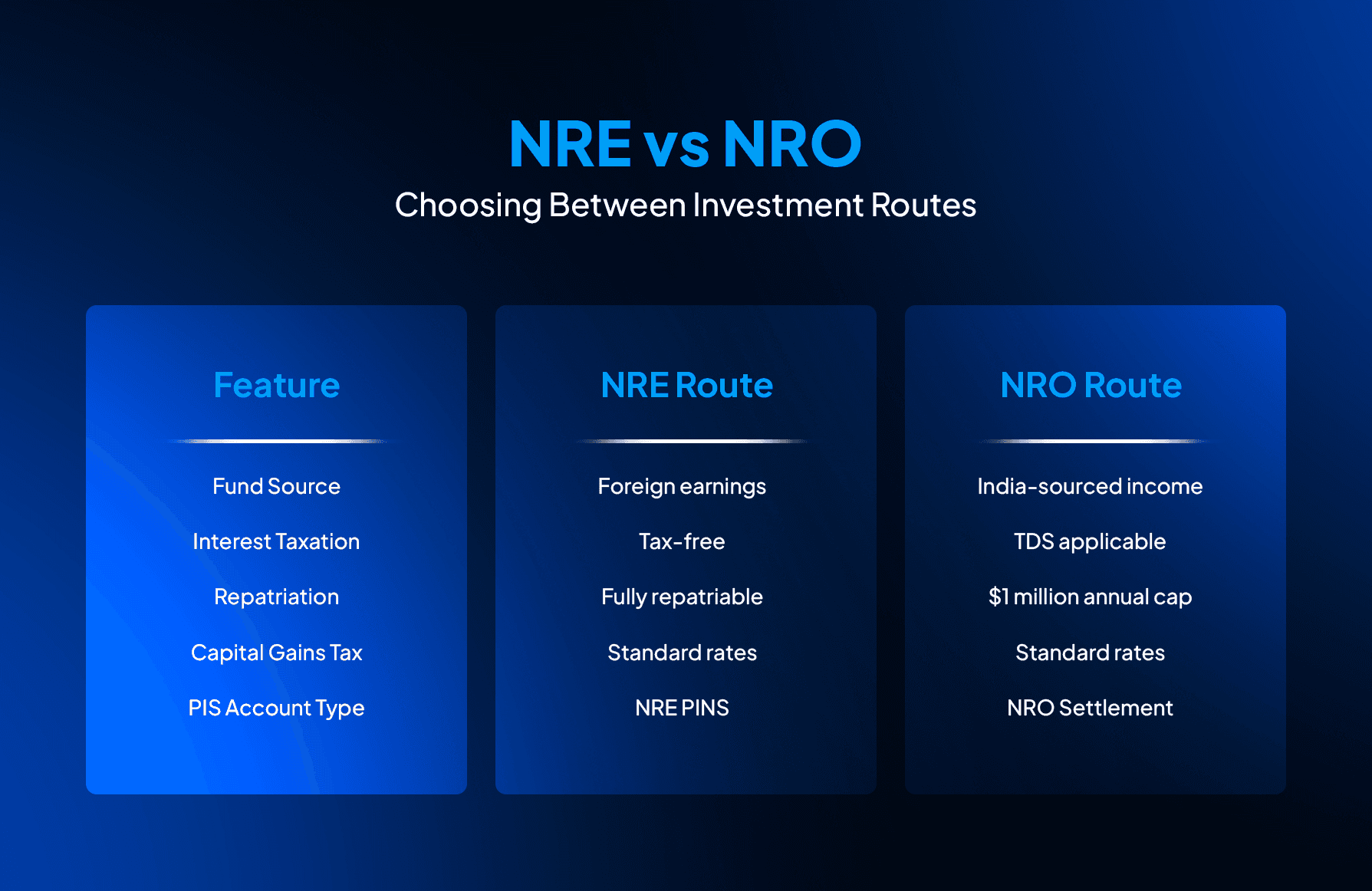
Foreign income sources suit NRE investments better. Full repatriation rights give maximum flexibility. Tax-free interest adds to overall returns.
India-sourced income belongs in NRO accounts by regulation. Rental income from Indian property must use this route. Annual repatriation caps work for many investors. Many NRIs maintain both account types strategically based on income sources.
Step-by-Step Account Opening Process
Account setup follows a specific sequence. Allow 3-4 weeks for complete setup.
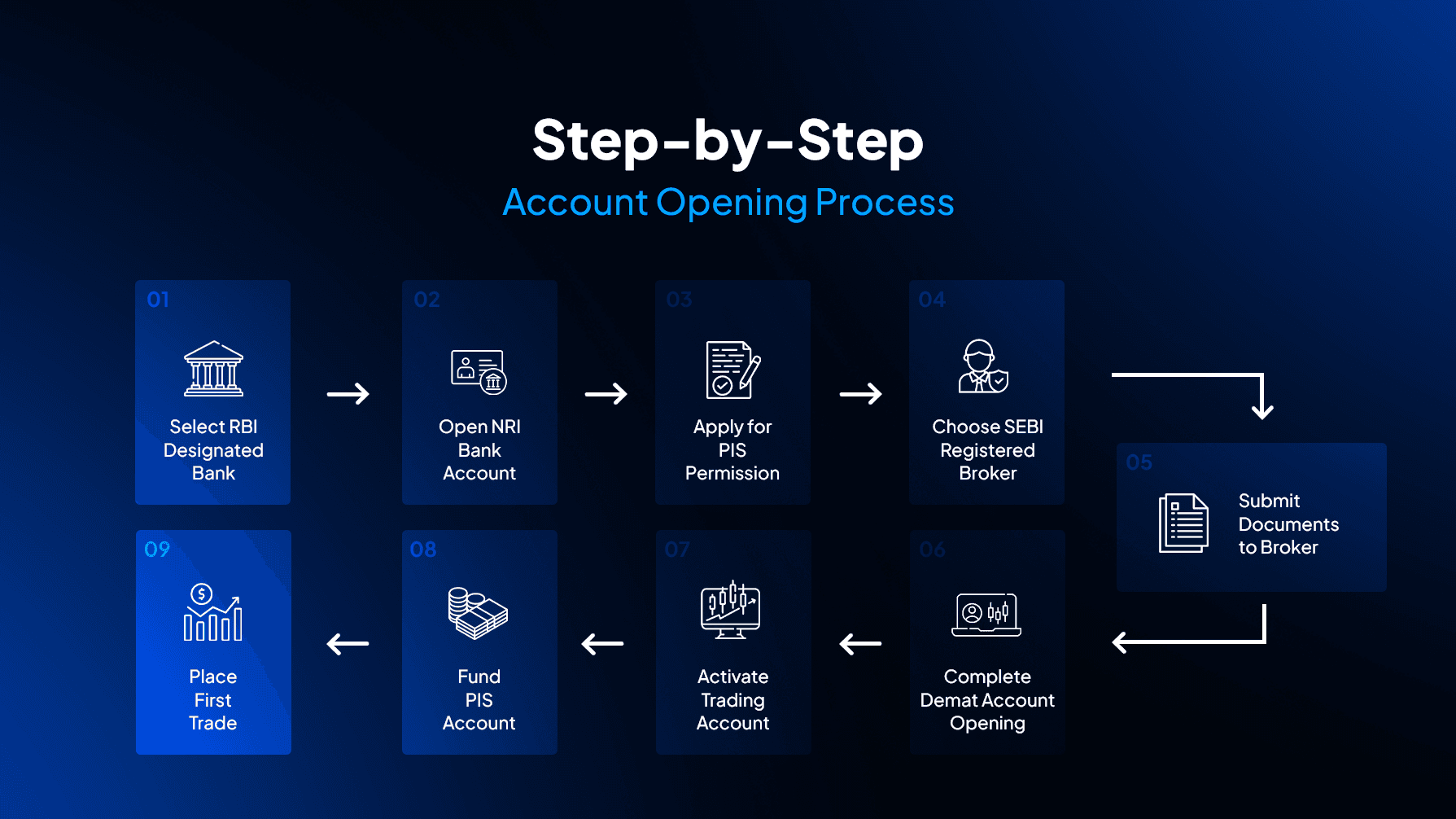
Step 1: Select RBI-Designated Bank - Not all banks offer PIS services. Major players include ICICI, HDFC, Kotak, Axis, and SBI. Digital account opening speeds up the process.
Step 2: Open NRI Bank Account - Submit passport, visa, PAN, and address proofs. Processing takes 7-10 working days. Decide between NRE and NRO based on fund sources.
Step 3: Apply for PIS Permission - Request PIS facility with your NRI account application. Banks submit permission request to RBI electronically. You receive unique PIS permission number and letter.
Step 4: Choose SEBI-Registered Broker - Compare brokerage rates, platform features, and customer support. Verify SEBI registration directly. Integrated 3-in-1 accounts simplify setup.
Step 5: Submit Documents to Broker - Include passport with visa, PAN card, address proof, bank statements, and PIS permission letter. Broker forwards documents to KRA agencies.
Step 6: Complete Demat Account Opening - Broker opens demat with NSDL or CDSL. Link this demat to your PIS bank account. Ensure account numbers match exactly.
Step 7: Activate Trading Account - Trading credentials arrive via email. Set strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication. Test platform features before actual trading.
Step 8: Fund PIS Account - Transfer money from NRE/NRO savings to PIS account. Only PIS account balance funds stock purchases. First funding takes 1-2 days.
Step 9: Place First Trade - Search for stocks on trading platform. Place limit orders during market hours 9:15 AM to 3:30 PM IST. Shares arrive in demat on T+1 settlement day.
Documentation Requirements
Proper paperwork determines approval speed. Missing documents cause rejections.
Identity Verification: Passport with all pages, PAN card, current visa or work permit proving NRI status
Address Proof: Recent utility bills less than 3 months old, foreign bank statements showing address, rental agreements
Financial Documentation: Last 6 months overseas bank statements establishing capacity and fund sources
Photographs: Recent passport-size photographs on white background, 4-6 copies needed
Attestation: Indian embassy or notary attestation. Some countries offer apostille certification.
Start document preparation 2-3 months before planned account opening. Digital copies suffice for initial applications.
Tax Implications: Capital Gains and TDS
Tax treatment varies by holding period. Understanding obligations helps plan returns better.
Capital Gains Tax
Holdings sold within 12 months qualify as short-term at twenty percent plus surcharge. Holdings beyond 12 months qualify as long-term. Gains up to Rs 1.25 lakh per year remain exempt. Amounts exceeding this face 12.5 percent tax.
TDS Process
Brokers or PIS banks deduct TDS automatically on every sale. Form 16A generates for each transaction. Collect TDS certificates quarterly. These support tax filings in both India and abroad.
Dividend Taxation
Companies deduct twenty percent TDS before paying dividends. Applies to both NRE and NRO holders. Dividend credits to linked account after deduction.
Filing Requirements
Indian income exceeding basic exemption mandates ITR-2 filing. Online filing through income tax portal works. Proper filing supports foreign tax credit claims. India has DTAA agreements with many countries preventing double taxation.
NRE route proceeds move abroad without additional tax. NRO route faces same capital gains TDS. Maintain transaction documentation for seven years minimum.
Common Challenges and Solutions
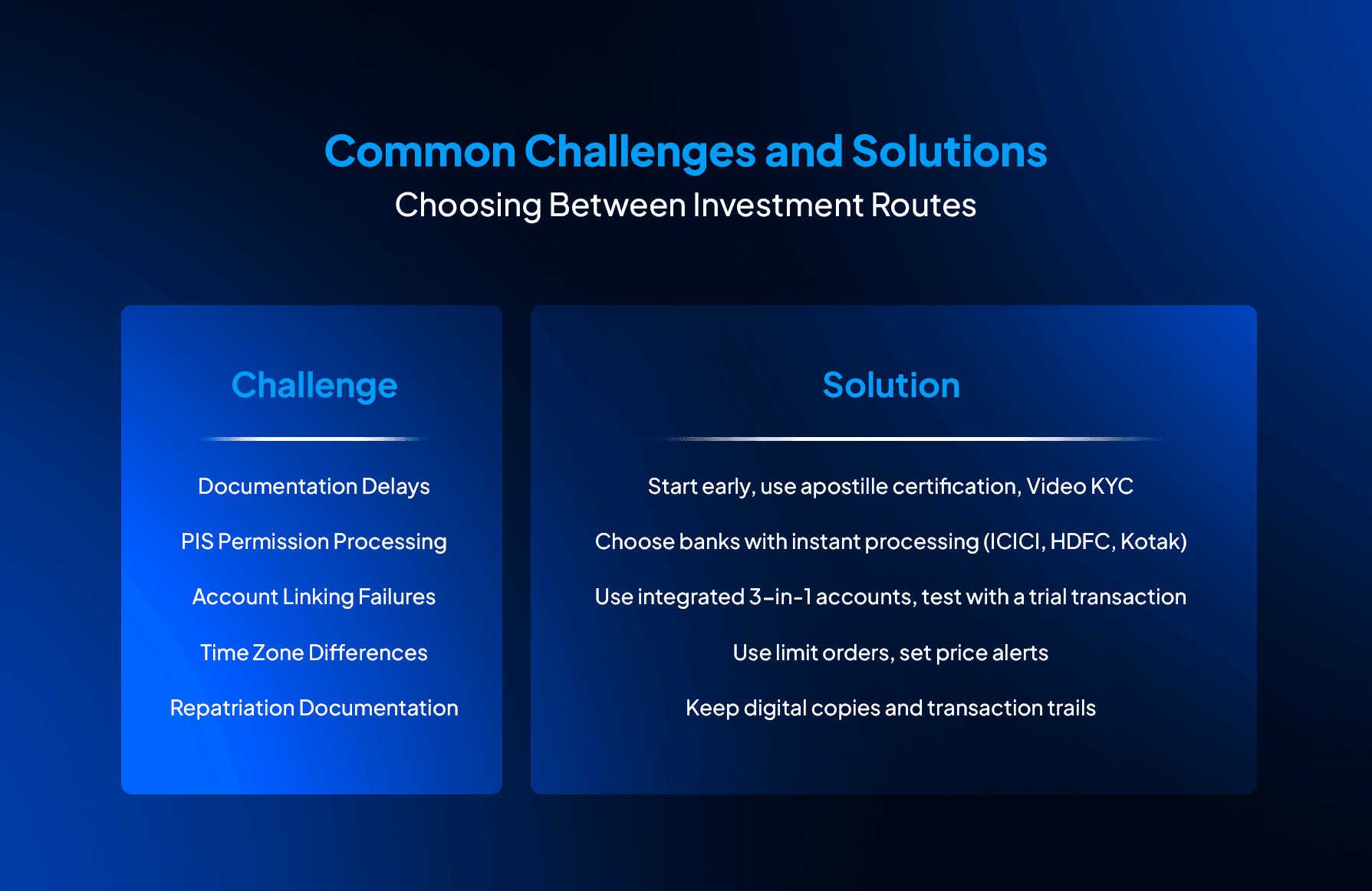
Documentation Delays
Embassy attestation takes weeks. Start preparation 2-3 months ahead. Use apostille certification where available. Video KYC bypasses some physical requirements.
PIS Permission Processing
Choose banks with automated processing. ICICI, HDFC, and Kotak offer instant permissions. Double-check application fields before submission.
Account Linking Failures
Use integrated 3-in-1 accounts from banks with broking tie-ups. Test system with small trial transaction. Keep account numbers documented for troubleshooting.
Time Zone Differences
Use limit orders instead of market orders. Set price alerts on mobile apps. Consider systematic investment approaches rather than active trading.
Repatriation Documentation
Maintain digital copies from day one. Create dedicated file system. Bank requests should include complete transaction trail proactively.
Time invested upfront prevents majority of problems. Well-prepared customers receive better service.
Why Should You Choose Ckredence Wealth for NRI Portfolio Management
Managing stock investments from abroad adds complexity. Time zone differences make active trading impractical. Professional management becomes necessary for serious wealth building.
We specialize in NRI investment management with complete FEMA and SEBI understanding. Our team handles regulatory changes proactively. You avoid mistakes that delay starts.
Services We Offer:
Customized investment strategies matching your risk profile and financial goals
Active portfolio management with systematic rebalancing as conditions change
Regular performance reporting with complete transparency on holdings
Dedicated relationship managers understanding overseas investor needs
Our Track Record:
₹805+ Crores in assets under management. 37 years of market experience across economic cycles. 376+ active clients rely on us. Four distinct investment approaches cover various conditions.
Compliance Support:
SEBI registration (INP000007164) provides investor protection. We handle all reporting requirements. Tax documentation support simplifies ITR filing.
Service Delivery:
Regular updates via email regardless of time zones. Video consultations accommodate your schedule. Digital platforms provide 24/7 access.
Professional management removes constant monitoring burden. Your wealth grows through disciplined strategies.
Ready to build wealth with expert guidance? Schedule a Consultation.
Conclusion
NRI access to Indian stock markets operates through well-defined regulatory channels. Success depends on proper account setup and compliance understanding.
Action Points:
Open NRE or NRO accounts based on fund sources before starting investment
Secure PIS permission as mandatory requirement for secondary trading
Choose SEBI-registered brokers offering complete NRI services
Maintain thorough documentation for tax filing and repatriation requests
Market participation from abroad builds wealth systematically. Professional guidance accelerates your journey while avoiding pitfalls.
FAQs
Can NRI invest in the Indian stock market without a PIS account?
PIS accounts are mandatory for secondary market trading only. IPO investments and mutual funds don't require PIS. NRO holders can make certain investments without PIS permissions.
How does portfolio management service differ from direct stock investing for NRIs?
PMS offers professional management with customized strategies for your goals. Direct investing means you make all decisions yourself. PMS requires minimum amounts typically starting at Rs 50 lakhs.
What is the minimum investment required for NRIs in Indian stocks?
No official minimum exists for stock purchases. Broker account opening minimums vary from zero to ten thousand. Practical trading starts around twenty-five thousand for proper diversification.
Are NRIs from USA and Canada allowed to invest in Indian equities?
Yes, NRIs from USA and Canada can invest freely. Some mutual funds restrict US or Canada NRIs due to FATCA. Direct equity investments face no country-specific restrictions.
Stock market regulations under FEMA 2000 permit Non-Resident Indians to purchase equity shares through Portfolio Investment Scheme accounts. RBI data shows NRI investment in Indian securities reached ₹14,01,673 crores as of December 2024 (Reserve Bank of India). NSE and BSE provide market access through designated bank channels with specific compliance requirements.
Do bank representatives give contradictory information about NRE versus NRO accounts for stock trading with repatriation rights?
Are PIS permission delays from RBI pushing back your investment timeline by 30-45 days despite having funds ready?
Does the mandatory delivery-based trading requirement limit your ability to capture intraday price movements in volatile markets?
Secondary market participation requires four linked accounts working together. Banks open PIS-designated accounts separate from regular NRI accounts. Brokers provide demat and trading accounts with restricted features. Each account serves a specific regulatory function affecting fund flow.
Key Takeaways
Portfolio Investment Scheme accounts through RBI-designated banks form the mandatory channel for buying and selling equity shares on NSE and BSE
NRE accounts provide full repatriation rights after capital gains tax while NRO accounts face annual transfer caps for moving proceeds abroad
Intraday trading prohibitions restrict NRIs to delivery-based purchases only with shares settling in demat accounts on T+1 timeline
Documentation requirements include passport with valid visa proof, PAN card, overseas address verification, and foreign bank statements
Individual holding caps limit any single NRI to five percent of company paid-up capital with total NRI investment restricted to ten percent
Tax deduction at source applies automatically on capital gains before crediting sale proceeds with different rates for holding periods
Account linking sequence matters: open bank account first, secure PIS permission second, then establish demat and trading access third
Can NRI Invest in Indian Stock Market
Yes, NRIs can purchase and sell equity shares under FEMA regulations administered by RBI. The Foreign Exchange Management Act provides the legal framework. SEBI governs trading conduct and market operations.
Non-Resident Indians access secondary markets through designated channels only. You cannot open regular resident trading accounts. The system requires specific account types with additional verification layers.
Regulatory Framework
RBI controls foreign exchange aspects through FEMA guidelines. Portfolio Investment Scheme falls under Schedule 3 of FEMA regulations. SEBI sets trading rules for all market participants. NRIs follow different guidelines compared to residents. Compliance checks happen at multiple levels.
Investment Routes Available
Two main routes exist for NRI equity investments. PIS route handles secondary market trading on stock exchanges. Non-PIS route serves IPO subscriptions and mutual fund investments. Your choice between NRE and NRO accounts determines repatriation rights later.
Key Investment Guidelines and Trading Options for NRIs
Trading permissions come with specific boundaries. RBI and SEBI impose these limits to prevent market manipulation.
1. Permitted Investment Instruments
Equity Shares: NRIs can buy shares of companies listed on NSE and BSE. Both repatriation and non-repatriation basis investments work.
Convertible Debentures: Debentures converting into equity shares are permitted. Holdings count toward overall investment limits.
Mutual Funds: MF investments don't need PIS accounts. Direct purchase through NRE or NRO accounts works.
IPO Subscriptions: Primary market investments bypass PIS requirements. Allotted shares later need PIS accounts if selling.
2. Sector Investment Restrictions
Atomic energy projects cannot receive foreign capital. Railways infrastructure falls under similar restrictions. Lottery and gambling businesses stay prohibited. Defense manufacturing requires government approval. Banking sector investments follow separate FDI guidelines.
3. Trading Restrictions
Delivery-Based Only: All purchases must settle into your demat account. T+1 settlement means shares transfer one day after trade date. Same-day buy and sell transactions get automatically blocked.
Shareholding Caps: No single NRI can own more than five percent of any company's paid-up capital. Total NRI ownership caps at ten percent of company capital. Companies can increase this to twenty-four percent through shareholder resolution.
Derivatives Trading: Futures and options need SEBI-registered custodian appointment. Only NRO accounts work for F&O trading. Equity and index derivatives are permitted instruments.
Account Requirements: NRE Account, NRO Account, and PIS Permission
Three account types form the foundation of NRI stock investments. Setting them up correctly prevents transaction failures.
NRE Account (Non-Resident External)
NRE accounts hold foreign earnings converted to rupees. Salaries from overseas jobs go here. Full repatriation rights remain tax-free in India. Interest earned avoids Indian income tax completely. Only capital gains tax applies when selling stocks.
NRO Account (Non-Resident Ordinary)
NRO accounts manage India-sourced income exclusively. Rent from Indian property goes here. Annual transfers abroad cap at one million US dollars. Interest faces tax deduction at source. Mixing foreign and Indian income violates regulations.
PIS-Designated Account Setup
Stock transactions require separate PIS-linked accounts. NRE holders need NRE PINS accounts. NRO holders need NRO settlement accounts. Only one PIS account permitted per NRI nationwide.
Banks apply to RBI for your PIS authorization. Approval results in a unique permission letter containing permission number and trading limits. Brokers need this letter before opening demat accounts.
Demat and Trading Account Linking
Your demat account must link to PIS bank account correctly. NRE demat connects with NRE PINS accounts. NRO demat links to NRO settlement accounts. Brokers provide trading platforms after account linking completes.
NRE vs NRO: Choosing Between Investment Routes
Your account choice affects taxes, fund movement, and compliance requirements.

Foreign income sources suit NRE investments better. Full repatriation rights give maximum flexibility. Tax-free interest adds to overall returns.
India-sourced income belongs in NRO accounts by regulation. Rental income from Indian property must use this route. Annual repatriation caps work for many investors. Many NRIs maintain both account types strategically based on income sources.
Step-by-Step Account Opening Process
Account setup follows a specific sequence. Allow 3-4 weeks for complete setup.

Step 1: Select RBI-Designated Bank - Not all banks offer PIS services. Major players include ICICI, HDFC, Kotak, Axis, and SBI. Digital account opening speeds up the process.
Step 2: Open NRI Bank Account - Submit passport, visa, PAN, and address proofs. Processing takes 7-10 working days. Decide between NRE and NRO based on fund sources.
Step 3: Apply for PIS Permission - Request PIS facility with your NRI account application. Banks submit permission request to RBI electronically. You receive unique PIS permission number and letter.
Step 4: Choose SEBI-Registered Broker - Compare brokerage rates, platform features, and customer support. Verify SEBI registration directly. Integrated 3-in-1 accounts simplify setup.
Step 5: Submit Documents to Broker - Include passport with visa, PAN card, address proof, bank statements, and PIS permission letter. Broker forwards documents to KRA agencies.
Step 6: Complete Demat Account Opening - Broker opens demat with NSDL or CDSL. Link this demat to your PIS bank account. Ensure account numbers match exactly.
Step 7: Activate Trading Account - Trading credentials arrive via email. Set strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication. Test platform features before actual trading.
Step 8: Fund PIS Account - Transfer money from NRE/NRO savings to PIS account. Only PIS account balance funds stock purchases. First funding takes 1-2 days.
Step 9: Place First Trade - Search for stocks on trading platform. Place limit orders during market hours 9:15 AM to 3:30 PM IST. Shares arrive in demat on T+1 settlement day.
Documentation Requirements
Proper paperwork determines approval speed. Missing documents cause rejections.
Identity Verification: Passport with all pages, PAN card, current visa or work permit proving NRI status
Address Proof: Recent utility bills less than 3 months old, foreign bank statements showing address, rental agreements
Financial Documentation: Last 6 months overseas bank statements establishing capacity and fund sources
Photographs: Recent passport-size photographs on white background, 4-6 copies needed
Attestation: Indian embassy or notary attestation. Some countries offer apostille certification.
Start document preparation 2-3 months before planned account opening. Digital copies suffice for initial applications.
Tax Implications: Capital Gains and TDS
Tax treatment varies by holding period. Understanding obligations helps plan returns better.
Capital Gains Tax
Holdings sold within 12 months qualify as short-term at twenty percent plus surcharge. Holdings beyond 12 months qualify as long-term. Gains up to Rs 1.25 lakh per year remain exempt. Amounts exceeding this face 12.5 percent tax.
TDS Process
Brokers or PIS banks deduct TDS automatically on every sale. Form 16A generates for each transaction. Collect TDS certificates quarterly. These support tax filings in both India and abroad.
Dividend Taxation
Companies deduct twenty percent TDS before paying dividends. Applies to both NRE and NRO holders. Dividend credits to linked account after deduction.
Filing Requirements
Indian income exceeding basic exemption mandates ITR-2 filing. Online filing through income tax portal works. Proper filing supports foreign tax credit claims. India has DTAA agreements with many countries preventing double taxation.
NRE route proceeds move abroad without additional tax. NRO route faces same capital gains TDS. Maintain transaction documentation for seven years minimum.
Common Challenges and Solutions

Documentation Delays
Embassy attestation takes weeks. Start preparation 2-3 months ahead. Use apostille certification where available. Video KYC bypasses some physical requirements.
PIS Permission Processing
Choose banks with automated processing. ICICI, HDFC, and Kotak offer instant permissions. Double-check application fields before submission.
Account Linking Failures
Use integrated 3-in-1 accounts from banks with broking tie-ups. Test system with small trial transaction. Keep account numbers documented for troubleshooting.
Time Zone Differences
Use limit orders instead of market orders. Set price alerts on mobile apps. Consider systematic investment approaches rather than active trading.
Repatriation Documentation
Maintain digital copies from day one. Create dedicated file system. Bank requests should include complete transaction trail proactively.
Time invested upfront prevents majority of problems. Well-prepared customers receive better service.
Why Should You Choose Ckredence Wealth for NRI Portfolio Management
Managing stock investments from abroad adds complexity. Time zone differences make active trading impractical. Professional management becomes necessary for serious wealth building.
We specialize in NRI investment management with complete FEMA and SEBI understanding. Our team handles regulatory changes proactively. You avoid mistakes that delay starts.
Services We Offer:
Customized investment strategies matching your risk profile and financial goals
Active portfolio management with systematic rebalancing as conditions change
Regular performance reporting with complete transparency on holdings
Dedicated relationship managers understanding overseas investor needs
Our Track Record:
₹805+ Crores in assets under management. 37 years of market experience across economic cycles. 376+ active clients rely on us. Four distinct investment approaches cover various conditions.
Compliance Support:
SEBI registration (INP000007164) provides investor protection. We handle all reporting requirements. Tax documentation support simplifies ITR filing.
Service Delivery:
Regular updates via email regardless of time zones. Video consultations accommodate your schedule. Digital platforms provide 24/7 access.
Professional management removes constant monitoring burden. Your wealth grows through disciplined strategies.
Ready to build wealth with expert guidance? Schedule a Consultation.
Conclusion
NRI access to Indian stock markets operates through well-defined regulatory channels. Success depends on proper account setup and compliance understanding.
Action Points:
Open NRE or NRO accounts based on fund sources before starting investment
Secure PIS permission as mandatory requirement for secondary trading
Choose SEBI-registered brokers offering complete NRI services
Maintain thorough documentation for tax filing and repatriation requests
Market participation from abroad builds wealth systematically. Professional guidance accelerates your journey while avoiding pitfalls.
FAQs
Can NRI invest in the Indian stock market without a PIS account?
PIS accounts are mandatory for secondary market trading only. IPO investments and mutual funds don't require PIS. NRO holders can make certain investments without PIS permissions.
How does portfolio management service differ from direct stock investing for NRIs?
PMS offers professional management with customized strategies for your goals. Direct investing means you make all decisions yourself. PMS requires minimum amounts typically starting at Rs 50 lakhs.
What is the minimum investment required for NRIs in Indian stocks?
No official minimum exists for stock purchases. Broker account opening minimums vary from zero to ten thousand. Practical trading starts around twenty-five thousand for proper diversification.
Are NRIs from USA and Canada allowed to invest in Indian equities?
Yes, NRIs from USA and Canada can invest freely. Some mutual funds restrict US or Canada NRIs due to FATCA. Direct equity investments face no country-specific restrictions.